The Frozen Embryo Transfer, commonly referred to as FET, is an important process in assisted reproduction technology (ART) which has assisted countless couples in achieving their dreams of becoming parents. What exactly is FET? And what is it that makes it different from traditional methods for transferring embryos? In this article we'll explore the process of freezing embryos and its benefits, disadvantages, as well as everything you should know about the frozen embryo transfer.
What is Embryo Transfer?
Before you dive into freezing embryo transfer it's essential to know the concept behind embryo transfer. In simple terms, embryo transfer refers to the process of inserting an embryo in the uterus of a woman in order to obtain pregnancy. It can be done with fresh embryos or frozen embryos. The main objective of embryo transfer is to provide the best conditions for successful implantation as well as a successful pregnancy.
What is FET?
Frozen embryo Transfer (FET) involves defrosting frozen embryos before transferring to the uterus. In contrast to fresh embryo transfer which transfers embryos immediately upon fertilization FET permits embryos to be kept to use later. This gives flexibility to the patient as well as the fertility clinic by allowing the time needed to prepare for hormones, recover of previous treatments or a better understanding of uterine issues.
The demand for FET has grown in recent years because of its high rate of success and lower risks as compared to fresh embryo transfer. Thanks to advances in freezing techniques, including vitrification, rate of survival for frozen embryos are similar to fresh embryos.
Frozen Embryo Transfer Procedure
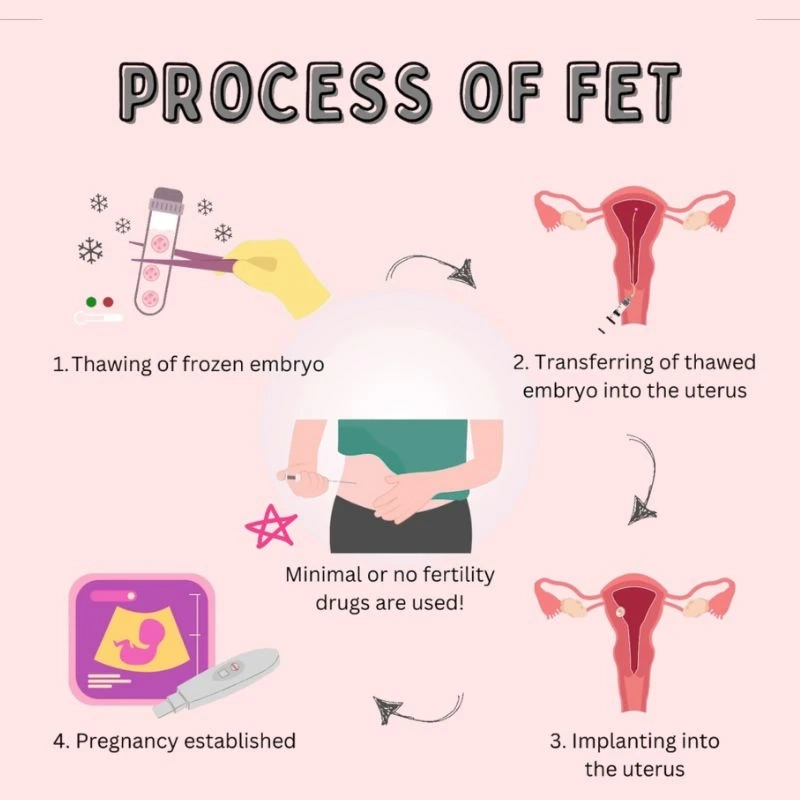
The procedure of freezing embryos is carefully designed to maximize the chance of a pregnancy that is successful. Here's an outline on the FET cycle:
- Prepare the Uterus: The first stage in the frozen embryo transfer process is to prepare the uterine liner. It could involve hormone therapy to increase the thickness of the endometrium, and to create an environment that is conducive to the embryo implantation.
- Monitors: During this period doctors carefully examine hormone levels as well as the amount of Uterine lining by using ultrasound scans.
- Thawing the embryos: After the uterus has been declared prepared then freezing the embryos is then carefully removed from the lab. The viability and the quality of the embryos is assessed prior to transfer.
- Transfer Procedure: The actual frozen embryo transfer process is easy and quick. Utilizing a catheter that is thin to transfer the selected embryo put in the uterus.
- Post-Transfer Treatment: Following the transfer patients are advised to take a short rest. The hormonal support continues to aid in the process of implantation. Pregnancy tests will be scheduled around two weeks after the transfer.
Advantages of Frozen Embryo Transfer
FET provides numerous positives over transfers of fresh embryos:
- The flexibility: Patients can choose the best time for their transfer, without having to rush.
- reduced Ovarian Hyperstimulation Risk Because embryos are frozen during development, Ovaries are able to heal after stimulation.
- Better Success in Certain cases: Some studies suggest that frozen embryo transfer cycles could be more successful regarding implantation and alive birth rate, specifically for specific patients.
- Chance to Test Genetics: FET allows time for preimplantation genetic testing in order to test for chromosomal anomalies.
Disadvantages of Frozen Embryo Transfer
Although it has its merits, FET also has potential negatives
- Extended Waiting Time: Patients may need to wait for months or weeks before being transferred.
- Sexual Side Effects Hormone therapy for preparing the uterus for delivery can result in mood swings, constipation, and other mild side effects.
- A slight increase in risk of some pregnancy-related complications: Some studies have identified slightly higher risk of preeclampsia-related conditions during frozen embryo pregnancy but the risks are quite low.
Understanding the FET Cycle
An embryo frozen is typically less demanding physically than a fresh one since the ovaries aren't required to be stimulated. This makes the procedure easier for patients and still ensuring high likelihood of successful. The process is highly individual by doctors who adjust the dosage of hormones and timing depending on the individual's needs and the quality of frozen embryos.
Key Takeaways
The frozen embryo transfer revolutionized fertility treatment, providing hope to couples infertile or who prefer to wait until they are pregnant. If you know the basics of FET as well as the procedure for freezing embryos and the frozen embryo transfer procedure patients are able to make informed decisions and plan physically and emotionally for the process ahead.
While there are a few minor downsides but the benefits of FET include the flexibility, less stress on the ovaries, as well as an opportunity for screening genetics are a popular option for the modern clinic for fertility.
If you're thinking of IVF or are waiting on frozen embryos for transfer Discussing this cycle of FET with your fertility expert will help you determine the most effective method for your particular situation. If you follow the correct direction and guidance the transfer of frozen embryos is a secure and effective way of building your family.