Innovation drives growth, and protecting those innovations is essential. Filing a patent application safeguards your intellectual property by granting exclusive rights to the inventor. In India, the patent application process is structured under the Indian Patent Act, offering inventors and businesses a secure pathway to protect their creations.
What Is a Patent Application?
A patent application in India is a formal request submitted to the Indian Patent Office to obtain legal rights over an invention. Once granted, the patent gives the inventor exclusive authority to produce, use, or license the invention for a specified period, usually 20 years.
Patent Application Process in India
The patent application process involves several steps to ensure the invention meets legal standards:
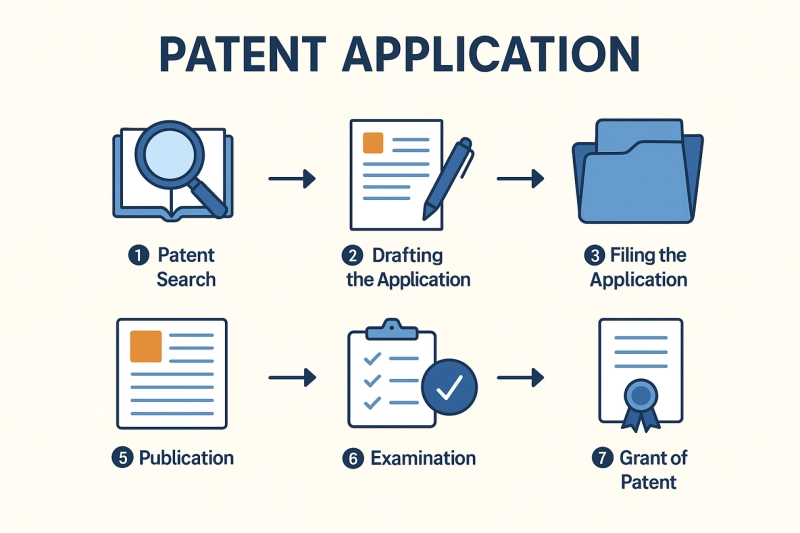
Patent Search – Conduct a prior art search to confirm that the invention is unique.
Drafting the Application – Prepare detailed specifications, claims, and diagrams explaining the invention.
Filing the Application – Submit the application to the Indian Patent Office, either physically or through the e-filing system.
Publication – Applications are published in the Patent Journal after 18 months from the filing date. Early publication can also be requested.
Examination – A request for examination must be filed. Examiners check novelty, inventive step, and industrial applicability.
Objections & Hearing – If objections arise, applicants must provide clarification or amendments.
Grant of Patent – Once all requirements are satisfied, the patent is granted and recorded in the register.
Patent Application Types in India
The Indian patent system allows different patent application types depending on the stage and jurisdiction:
Provisional Application – Filed when the invention is not fully developed, giving the applicant 12 months to file a complete specification.
Ordinary Application – Filed directly with a complete specification without any priority claim.
Convention Application – Filed in India within 12 months of applying in a convention country, claiming priority from the first application.
PCT International Application – A global application under the Patent Cooperation Treaty, enabling applicants to seek protection in multiple countries.
PCT National Phase Application – Entry into India after filing an international PCT application.
Divisional Application – Filed when an invention contains multiple claims that need separation.
Patent of Addition – Filed for improvements or modifications of an already patented invention.
Why Patent Applications Matter
Patents provide inventors with security, commercial value, and recognition. A strong patent portfolio not only prevents competitors from exploiting innovations but also enhances the credibility of a business in the marketplace.
FAQs on Patent Applications in India
Q1: How long does it take to get a patent in India?
It generally takes 2–4 years, depending on examination and opposition proceedings.
Q2: Can a patent application be filed online in India?
Yes, India allows e-filing of patent applications for faster and more convenient submissions.
Q3: What is the validity of a granted patent in India?
Patents are valid for 20 years from the filing date, subject to annual renewal fees.
Q4: Can I file a patent application without a prototype?
Yes, as long as the invention can be described clearly and meets patentability criteria.
Q5: Who can apply for a patent in India?
An individual inventor, a group of inventors, or an assignee such as a company can apply.
For expert guidance on filing a patent application in India or navigating the patent application process, AMD LAW INDIA provides tailored support for innovators and businesses.