Nurturing Healing: A Comprehensive Guide to Wound Care and Diabetes!
Wound care is a critical aspect of healthcare, pivotal in preventing complications and promoting overall well-being. For individuals with diabetes, effective wound care becomes even more crucial due to the heightened risk of chronic wounds and delayed healing. This article explores the significance of wound care, innovative solutions, and the unique challenges injuries pose in individuals with diabetes.
Understanding Wound Care:
Wound care is a multidimensional approach encompassing various stages, from immediate first aid to long-term management. The primary goals include preventing infection, minimizing pain, and promoting optimal healing. Effective wound care involves thorough cleaning, proper dressing, and consistent monitoring.
Antimicrobial Dressings for the Best Wound Care Solutions
In recent years, advancements in wound care solutions have revolutionized the approach to treating various types of wounds. From traditional dressings to cutting-edge technologies, healthcare professionals have multiple options to address wound care solutions more efficiently.
Antimicrobial dressings have gained popularity for their ability to combat infection directly at the wound site. Silver-infused bandages, for example, have proven antimicrobial properties, reducing the risk of bacterial contamination and promoting a sterile environment conducive to healing.
Biological Dressings:
Biological dressings from human or animal tissues mimic the natural wound-healing process. These dressings can accelerate healing by providing a scaffold for tissue regeneration and promoting cell growth.
Advanced Therapies:
Emerging therapies such as growth factors and stem cell treatments show promise in promoting accelerated wound care ulcer. These approaches enhance the body’s natural regenerative capabilities, providing new avenues for addressing complex wounds.
Wound Care in Diabetic Ulcers:
Diabetes poses unique challenges to wound care, primarily due to its impact on the circulatory and nervous systems. Diabetic ulcers, often occurring on the feet, can lead to severe complications if not managed promptly and effectively.
Neuropathy and Peripheral Arterial Disease:
Individuals with diabetes frequently experience neuropathy (nerve damage) and peripheral arterial disease (reduced blood flow). These conditions diminish the ability to sense pain and impede adequate blood supply to wounds, hindering the body’s natural healing processes.
Preventive Measures:
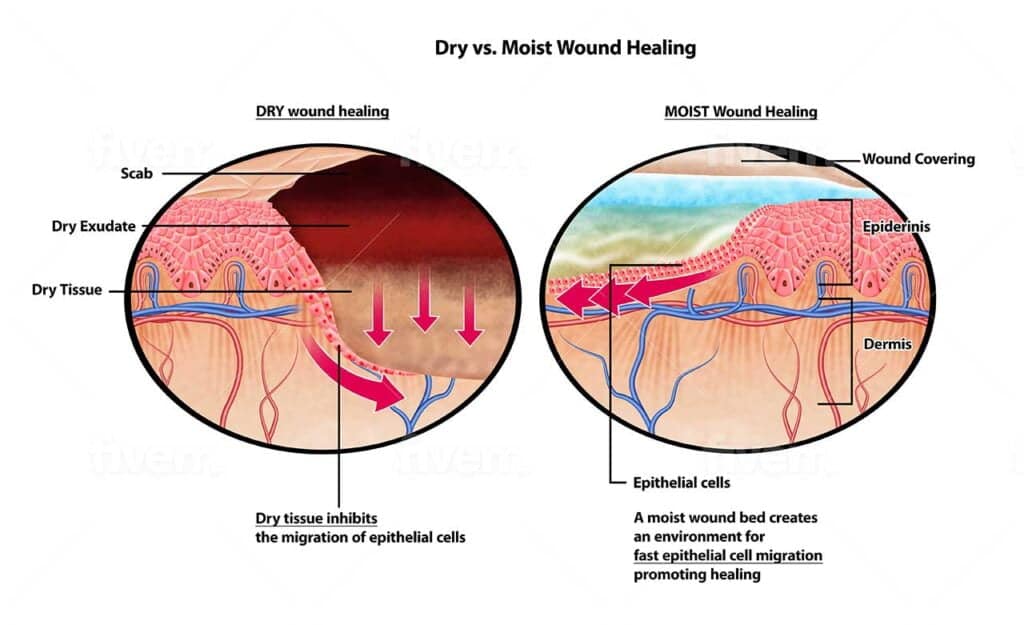
Given the increased susceptibility to foot ulcers in diabetes, preventive measures are crucial. Regular foot inspections, proper footwear, and moisture control are essential components of a comprehensive approach to preventing ulcers in diabetic individuals.
Wound Healing and Diabetes:
Wound healing and diabetes is often compromised due to a combination of factors. High blood sugar levels can impair immune function and hinder the formation of new blood vessels, essential for delivering nutrients to the wound site.
Wound healing and diabetes is often compromised due to a combination of factors.
Delayed Inflammatory Response:
Diabetes can lead to a delayed inflammatory response, the initial stage of wound healing. This delay can result in a prolonged inflammatory phase, increasing the risk of infection and complicating the overall healing process.
Impaired Collagen Synthesis:
Collagen, a key component of connective tissues, is vital for wound healing. Diabetes can impair collagen synthesis, weaken scar tissue formation, and increase susceptibility to wound complications.
Hyperglycemia and Infection Risk:
Persistent hyperglycemia in diabetes creates an environment conducive to bacterial growth, elevating the risk of infection in wounds. Therefore, controlling blood sugar levels is a critical aspect of managing diabetic wounds.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, wound care is an integral part of healthcare, with unique considerations for individuals with diabetes. Advances in wound care solutions provide a spectrum of options for healthcare professionals to address wounds more effectively. For those with diabetes, proactive and specialized wound care is essential to mitigate the increased risk of complications and support optimal healing. As research continues to unfold, the intersection of wound care and diabetes holds promise for improved outcomes and a better quality of life for individuals managing these conditions.
