eCommerce Product Cannibalization

Introduction
In the dynamic landscape of eCommerce, understanding the nuances between product cannibalization and internal cannibalization is crucial for strategic decision-making.
With the rise of eCommerce scraping services and advanced eCommerce data collection techniques, businesses now have access to vast amounts of data to inform their strategies.
Product cannibalization in retail refers to the scenario where sales of one product diminish the sales of another similar product within the same company’s portfolio.
On the other hand, internal cannibalization occurs when introducing a new product within a company’s lineup decreases the sales of its existing products. This distinction is vital for eCommerce businesses aiming to optimize their product offerings and maximize profitability.
By delving into the intricacies of eCommerce product data scraping and analysis, companies can gain insights into consumer behavior, market trends, and competitive dynamics, enabling them to mitigate the risks associated with cannibalization and capitalize on growth opportunities.
What is Product Cannibalization?
Product cannibalization occurs in retail when introducing or promoting a new product within a company’s portfolio decreases sales or demand for an existing product.
This phenomenon typically arises when the new product competes directly with an established product from the same company, offering similar features, functions, or benefits to the target audience.
As a result, rather than expanding the overall market share or customer base, the new product “cannibalizes” the sales of the existing product, leading to a redistribution of revenue within the company.
While product cannibalization can sometimes be a strategic move to capture market share or cater to evolving consumer preferences, it can pose challenges such as reduced profitability, brand dilution, and inventory management issues.
Thus, understanding and managing product cannibalization is essential for retailers to optimize their product mix, pricing strategies, and overall business performance.
Let’s Understand this using an example:
A fictional electronics company, TechGizmo, renowned for its cutting-edge smartphones. TechGizmo unveils a revolutionary model, the “TechGizmo X,” brimming with advanced camera technology and a battery life that’s a game-changer. However, TechGizmo already has a star in its product lineup, the “TechGizmo Y,” which has been a consistent performer.
Upon the release of the TechGizmo X, some customers considering purchasing the TechGizmo Y may opt for the newer model instead because of its superior features. As a result, sales of the TechGizmo Y started to decline, indicating product cannibalization.
In this scenario, introducing the TechGizmo X disrupts the sales of the TechGizmo Y within TechGizmo’s product lineup. While the TechGizmo X may attract new customers and generate revenue, the decline in sales of the TechGizmo Y significantly affects the overall profitability and market positioning of TechGizmo’s product portfolio, a matter of grave concern.
Recognizing the challenge, TechGizmo must swiftly adapt its marketing strategies, pricing, or product differentiation to counter the adverse effects of product cannibalization. This proactive approach is crucial to maintaining a healthy balance between its product offerings and safeguarding its market position.
Which are the Factors that Lead to Product Cannibalization?
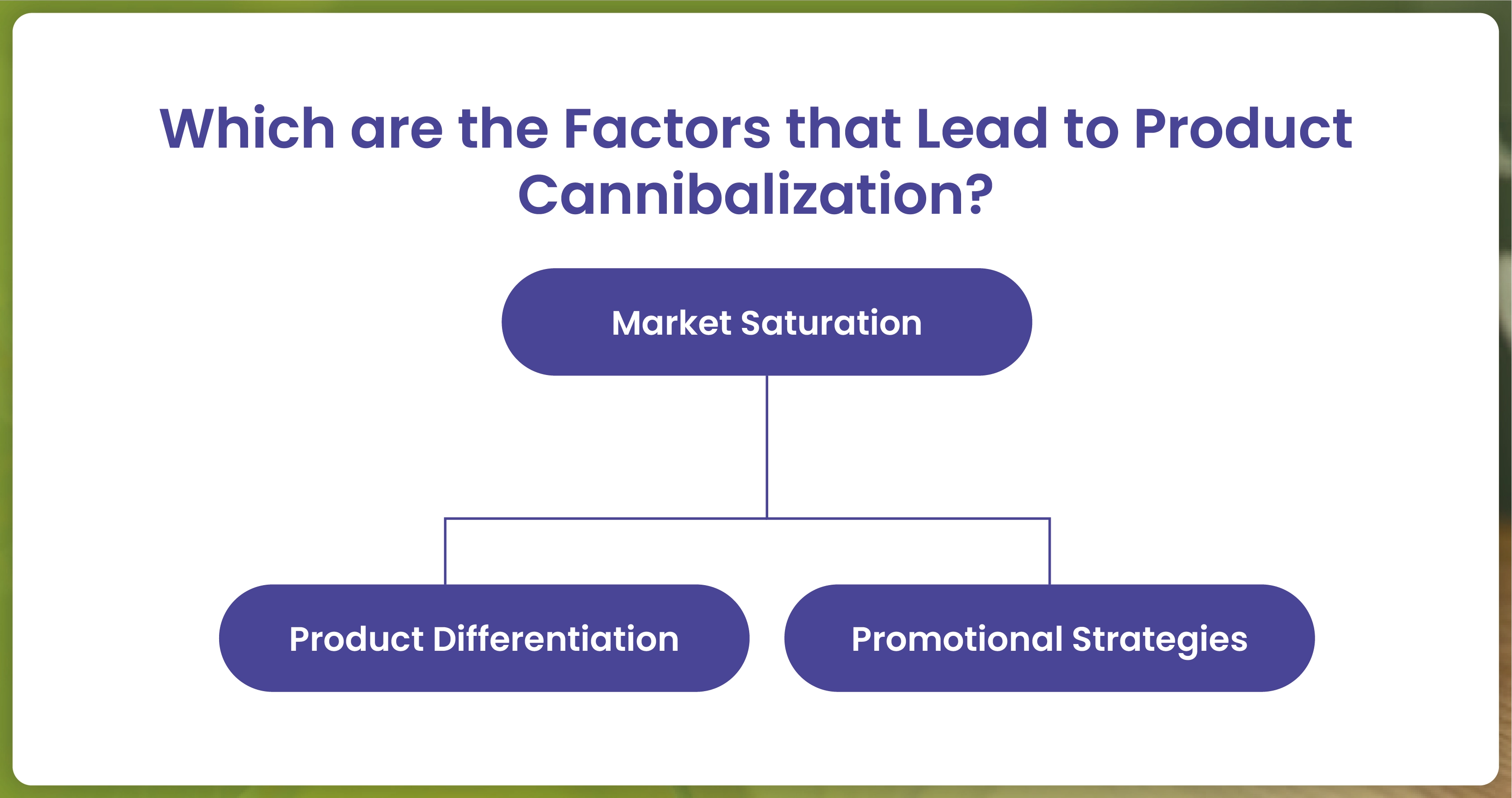
Product cannibalization in retail is a complex phenomenon influenced by various factors, each contributing to consumer behavior and market dynamics shifts.
Grasping these factors is beneficial and crucial for businesses involved in eCommerce scraping and data collection services.
It equips them with the knowledge to manage and mitigate the risks associated with cannibalization effectively.
Market Saturation: A market flooded with similar products from the same company can be a breeding ground for product cannibalization. The introduction of a new product can lead to a shift in consumer preferences, cannibalizing sales of existing ones.
Overlapping Target Audience: When new products cater to the same target audience as existing ones, they can inadvertently compete for the same customer base. This competition can lead to product cannibalization, affecting the sales of both products.
Product Differentiation: Insufficient differentiation between products can make it challenging for consumers to distinguish between them, resulting in cannibalization as they opt for whichever product more effectively meets their needs.
Promotional Strategies: Promoting new products excessively without clear differentiation from existing ones can inadvertently cannibalize sales of the latter.
By leveraging eCommerce scraping services and scrape internal cannibalization techniques, businesses can gain insights into consumer preferences, market trends, and competitive dynamics.
This data-driven approach enables them to refine their product strategies, optimize pricing, and develop targeted marketing campaigns to minimize the impact of product cannibalization on their bottom line.
What is Deliberate Product Cannibalization?
Deliberate product cannibalization occurs when a company intentionally introduces a new product into the market, understanding that it will cannibalize the sales of an existing product within its own lineup.
This strategic decision is often made to maintain or enhance the company’s overall market position, respond to changing consumer preferences, or capitalize on emerging market trends.
By cannibalizing its products, a company can prevent competitors from capturing market share or address internal challenges such as aging product lines.
Real-Life Example
Apple Inc. and its iPhone product line are real-life examples of deliberate product cannibalization.
Apple’s strategic foresight was evident when it introduced the iPhone SE in 2016, a move that deliberately cannibalized the sales of its higher-priced flagship models like the iPhone 6s and iPhone 6s Plus. The iPhone SE offered similar performance and features to the flagship models but at a significantly lower price point, a decision that made it more accessible to budget-conscious consumers.
Despite the risk of cannibalizing sales of its higher-margin flagship models, Apple strategically launched the iPhone SE to target a different segment of the market—those seeking a more affordable iPhone option. This move was aimed at not just maintaining but expanding its smartphone market share, particularly in regions where lower-priced smartphones are popular.
Apple’s deliberate cannibalization strategy with the iPhone SE allowed the company to maintain its market dominance and appeal to a broader range of consumers. The resounding success of the iPhone SE demonstrated how strategic product cannibalization can significantly contribute to a company’s overall growth and market position.
How to Calculate Product Cannibalization?
Calculating product cannibalization in retail involves systematically analyzing sales data to quantify how introducing a new product impacts existing product sales within a company’s product portfolio.
Leveraging eCommerce scraping services and eCommerce data collection techniques can provide retailers with the necessary data to assess and manage product cannibalization accurately. Let’s understand the process:
Identification of Susceptible Products: The first step in understanding product cannibalization is to identify the products within the retail lineup most likely to be affected. These products should share features, target demographics, or functionality similarities with the newly introduced product. This initial identification sets the stage for a more focused analysis of the impact of the new product.
Data Collection: The cornerstone of calculating product cannibalization is the comprehensive gathering of historical sales data. This is where eCommerce scraping services and data collection techniques come into play, providing a wealth of information for both the existing and the newly introduced products. This data must span a sufficient timeframe before and after the introduction of the new product to ensure accurate analysis.
Comparison of Sales Performance: Compare the sales performance of the existing products before and after introducing the new product. Calculate the sales volume or revenue difference for each existing product during these periods.
Calculation of Cannibalization Rate: Determine the percentage decrease in sales for each existing product attributed to the launch of the new product. This can be calculated by dividing the decrease in sales of each existing product by its pre-launch sales volume.
Aggregation of Cannibalization Rates: To assess the overall impact of the new product on the existing product line, aggregate the individual cannibalization rates across all affected products.
Analysis and Decision-Making: The final stage of the process is the most crucial. It’s here that the results of the analysis are interpreted and used to inform decision-making. This includes decisions on pricing strategies, product positioning, and marketing efforts. By making adjustments based on the analysis, retailers can effectively manage the effects of product cannibalization and optimize overall profitability in the retail landscape.
How Can One Prevent Product Cannibalization?
Preventing product cannibalization in retail requires strategic planning and proactive measures to minimize the impact of new product introductions on existing product lines.
Leveraging eCommerce scraping services and scrape product cannibalization techniques can provide valuable insights to inform these prevention strategies.
Differentiate Products: Emphasize the benefits of ensuring that each product within the retail lineup offers unique features, benefits, or target demographics. Clear differentiation helps minimize direct competition and instills confidence in retailers, reducing the likelihood of cannibalization.
Market Segmentation: Highlight the power of segmenting the target market based on factors such as price sensitivity, product preferences, and purchasing behavior. By offering products tailored to specific market segments, retailers can feel empowered, avoiding cannibalization by catering to distinct consumer needs.
Strategic Pricing: Reassure retailers about the effectiveness of pricing strategies that differentiate products based on value propositions and target markets. Price adjustments can effectively mitigate cannibalization by directing consumers toward products that offer the best value for their needs.
Cross-Selling and Upselling: Encourage cross-selling and upselling opportunities to promote complementary products rather than directly competing ones. By bundling products or offering discounts on related items, retailers can incentivize customers to purchase multiple products without cannibalizing sales.
Continuous Monitoring: Monitor sales data and market trends using eCommerce data collection techniques. By staying informed about changes in consumer behavior and competitive dynamics, retailers can proactively adjust their strategies to prevent product cannibalization before it occurs.
Conclusion
Preventing product cannibalization in retail is crucial for maintaining profitability and market competitiveness. Actowiz Solutions offers advanced eCommerce scraping services and data collection techniques to empower retailers to make informed decisions.
Retailers can effectively mitigate cannibalization risks by strategically differentiating products, segmenting markets, and monitoring sales data.
Stay ahead in the retail landscape with Actowiz Solutions and optimize your product offerings for sustained success. Contact us today to leverage our expertise and drive your business forward. You can also reach us for all your mobile app scraping, instant data scraper and web scraping service requirements.
sources >> https://www.actowizsolutions.com/manage-product-cannibalization-in-ecommerce.php
Tag : #eCommerceProductCannibalization
#DeliberateProductCannibalization
#ProductCannibalization
#RetailProductCannibalization
#eCommerceDataCollection

