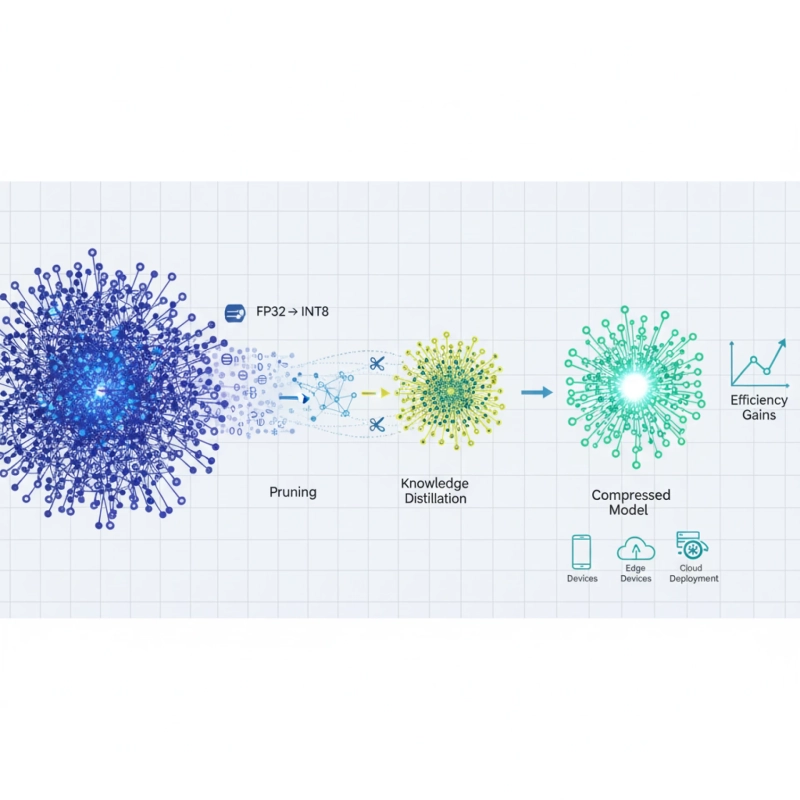
Without losing performance, compressing billion-parameter language models
Large language models (LLMs) like GPT-4 are growing at an exponential rate, which has opened up new AI possibilities. However, their huge size—often more than a billion parameters—makes them too expensive to use in real-world applications. This poses a significant challenge: how can we utilize the capabilities of these models while ensuring their practicality for extensive application? The answer is to use advanced model compression methods that cut down on size and processing power while keeping performance the same or even improving it.
The Need for Compression
Models with a billion parameters need a lot of computing power, memory, and energy. This means that only organizations with huge budgets for infrastructure can use them, and it raises environmental concerns. Also, because of latency problems, they aren't good for real-time applications like voice assistants or interactive systems. Model compression solves these problems by making smaller, faster versions of models that still have the same level of intelligence as their bigger versions.
Key Compression Techniques
1. Quantization
Quantization lowers the accuracy of model weights, usually changing them from 32-bit or 16-bit floating-point numbers to 8-bit or 4-bit integers. This easy but effective method can cut the size of a model by 75% or more with very little loss of accuracy. Quantization has become more effective thanks to advanced methods like GPTQ and AWQ. This means that models can run well on consumer hardware.
2. Pruning
This method gets rid of unnecessary parameters or whole neural connections that don't add much to the model's output. Pruning can cut the size of a model by 30% to 50% while keeping its performance by systematically finding and removing these "unimportant" weights. Modern methods focus on structured pruning that keeps hardware-friendly patterns for fast inference.
3. Knowledge Distillation
In this strong paradigm, a smaller "student" model learns to act like a bigger "teacher" model. The student learns not only from the initial training data but also from the teacher's outputs and internal representations, frequently attaining similar performance at a significantly reduced scale.
4. Low-Rank Approximation
This method breaks down large weight matrices into smaller, lower-rank parts, which cuts down on the number of parameters while keeping the important transformations that the original matrices did.
Advanced Approaches and Innovations
Recent research has yielded progressively advanced compression techniques:
Sparse Expert Models like Mixture of Experts (MoE) only use parts of the network for each input. This cuts down on computing costs while keeping a lot of parameters for storing knowledge.
With structural re-parameterization, you train a model with one architecture and then change it to a more efficient one for inference. This separates the structures for training and deployment.
Dynamic compression techniques change the amount of compression based on how complicated each input is. They give more resources to cases that are hard and less to cases that are easy.
Applications and Impact
Successful model compression makes many useful applications possible:
- Edge Deployment: Using advanced AI on mobile devices and built-in systems
- Real-time Inference: Giving interactive apps and chatbots the power to respond.
- Cost-effective Scaling: Using several smaller, more specialized models instead of one big, general model
- Democratization: Giving businesses access to cutting-edge AI without needing a lot of computing power
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite significant progress, compression still faces challenges including:
- Keeping up performance on tasks that require complex reasoning
- Keeping the model strong and calibrated
- Effectively dealing with different languages and domains
- Creating standard evaluation benchmarks
Future research will concentrate on automated compression pipelines, the theoretical underpinnings of compression efficacy, and methodologies that tailor compression strategies to particular deployment contexts.
Conclusion
Model compression is one of the most important areas of research for making AI work in real life. As LLMs get bigger and better, it will be more and more important to find ways to compress them so that they are easy to use, cheap, and long-lasting. Researchers are not just trying to make models smaller; they are also trying to make advanced AI useful for the world.