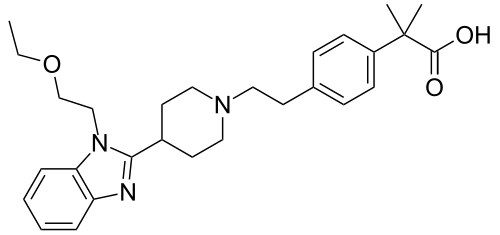
Bilastine: Uses, Interactions, and Mechanism of Action
In the crowded world of antihistamines, Bilastine stands out as a modern, non-sedating agent used for the treatment of allergic conditions. Approved in over 100 countries, this second-generation antihistamine is gaining popularity due to its favorable safety profile and effectiveness in relieving allergic symptoms without causing drowsiness. This article explores the key aspects of Bilastine — its uses, interactions, and mechanism of action.
What is Bilastine?
Bilastine is a second-generation H1-antihistamine used to treat allergic rhinitis (both seasonal and perennial) and chronic idiopathic urticaria. It is known for its selectivity, long duration of action, and lack of sedation, making it a preferred choice in daily allergy management.
Uses of Bilastine
Bilastine is indicated for the relief of symptoms associated with:
1. Allergic Rhinitis
- Sneezing
- Nasal congestion
- Runny nose
- Itchy eyes and nose
2. Chronic Idiopathic Urticaria
- Persistent hives
- Redness
- Itching and swelling
Key Benefits:
- Works within 1 hour of administration
- Provides relief for up to 24 hours
- Non-sedating and does not impair driving or cognitive function
Mechanism of Action
Bilastine works by selectively blocking peripheral H1 histamine receptors, which are responsible for allergic symptoms like swelling, redness, and itchiness. When allergens trigger the immune system, histamine is released from mast cells. Bilastine binds to H1 receptors, preventing histamine from exerting its effects.
Pharmacological Highlights:
- Does not cross the blood-brain barrier significantly, reducing the risk of sedation.
- No significant anticholinergic effects, which are commonly seen with first-generation antihistamines.
Drug Interactions
Although Bilastine has a relatively low interaction potential, certain substances may affect its absorption and efficacy:
1. Food and Fruit Juice
- Bilastine’s absorption is reduced when taken with food, especially fruit juices like grapefruit, apple, or orange juice.
- Recommendation: Take Bilastine on an empty stomach — either 1 hour before or 2 hours after a meal or juice.
2. P-glycoprotein Inhibitors
- Drugs like ketoconazole, erythromycin, diltiazem, and cyclosporine may increase plasma concentrations of Bilastine by inhibiting its transport.
- Clinical Impact: Usually not significant in healthy individuals, but caution is advised in people with renal impairment.
3. CNS Depressants
- Although Bilastine is non-sedating, concurrent use with alcohol or other central nervous system depressants may rarely cause drowsiness.
Dosing and Administration
- Adults and children ≥12 years: 20 mg once daily
- Should be taken on an empty stomach
- Not recommended in patients with severe renal impairment if co-administered with P-gp inhibitors
Safety and Side Effects
Bilastine is generally well-tolerated. Common side effects (typically mild) may include:
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Abdominal pain
- Drowsiness (rare)
It does not significantly affect the heart (no QT prolongation), liver, or kidneys in healthy individuals.
Conclusion
Bilastine offers effective allergy relief with minimal side effects, positioning itself as a reliable option for patients seeking a non-drowsy antihistamine. Its once-daily dosing, rapid onset, and long-lasting action make it particularly convenient for individuals managing chronic allergic conditions.
Whether you're dealing with seasonal allergies or chronic hives, Bilastine is a modern antihistamine worth considering — provided it’s taken correctly and with awareness of potential interactions.
URL: For more information, visit Vasista Pharma: Bilastine: Uses, Interactions, and Mechanism of Action