H.264 vs. H.265: 12 Facts You Should Know for Video Editing and Streaming
In recent years, we have witnessed breakthroughs in video playback technology as a result of the increasing popularity of videos. A video codec is an example of such technology, essential for a fluid watching experience. Currently, H.264 and H.265 are two of the most widely utilized video codecs. H.264 vs H.265, which one is better and what’s the difference? Let’s find out the answers in this blog.
What Is H.264 Codec (AVC)?
We’ve all experienced it: watching a movie, sports event, or Internet video when all of a sudden the screen freezes or the quality degrades. This sudden drop in quality is really annoying no matter what you’re watching. That’s why video codecs come into daily use.
The most widely adopted video compression standard at the moment is H.264, often known as “Advanced Video Coding” (AVC) or MPEG-4 Part 10. It was first made available in 2004 as a significantly improved version of its forerunners.
H.264 has the ability to significantly reduce video bitrates without largely lowering the video quality compared to earlier codecs. Exactly because of this highly efficient video encoding, H.264 has become the most popular codec ever.
Almost all current protocols, such as RTSP (Real Time Streaming Protocol), HLS Streaming, MPEG-DASH, HDS Streaming, and others, support H.264.
What Is H.265 Codec (HEVC)?
H.265 is a more recent video compression standard and, in many aspects, an improvement over H.264. It is also known as “High-Efficiency Video Coding” (HEVC) or MPEG-H Part 2. It was released in 2013, but it still has a long way to go before it is as well-known as AVC.
Higher efficiency necessitates better (and more costly) hardware than HEVC’s predecessor. As a result, rather than the general population, professional broadcasters and streamers still use it the most.
Today’s most popular video streaming protocols, such as HLS, MPEG-TS, and RTSP, all support H.265.
H.264 vs H.265: What’s the Difference?
It’s time to compare them now that we’ve gone over the fundamentals of each of these codecs. Here is a side-by-side comparison of H.264 vs H.265.
H.264 (AVC)
H.265 (HEVC)
Supported Video Formatsmkv, mp4, qtff, asf, avi, mxf, ps, ts, m2ts, evo, 3gp, f4vmkv, mp4, qtff, asf, avi, mxf, ps, ts, 3gpBandwidth Required for Video Encoding480p — 1.5 Mbps
720p — 3 mpbs
1080p — 6 Mbps
4K — 32 mbps480p — 0.75 Mbps
720p — 1.5 mpbs
1080p — 4 Mbps
4K — 15 mbpsRequired Bandwidth for 4K Broadcasting32 mbps15 mbpsIntraframe Prediction9 modes35 modesMotion Compensation TechnologyVector predictionAdvanced vector predictionColor Depth8 bit10 bit
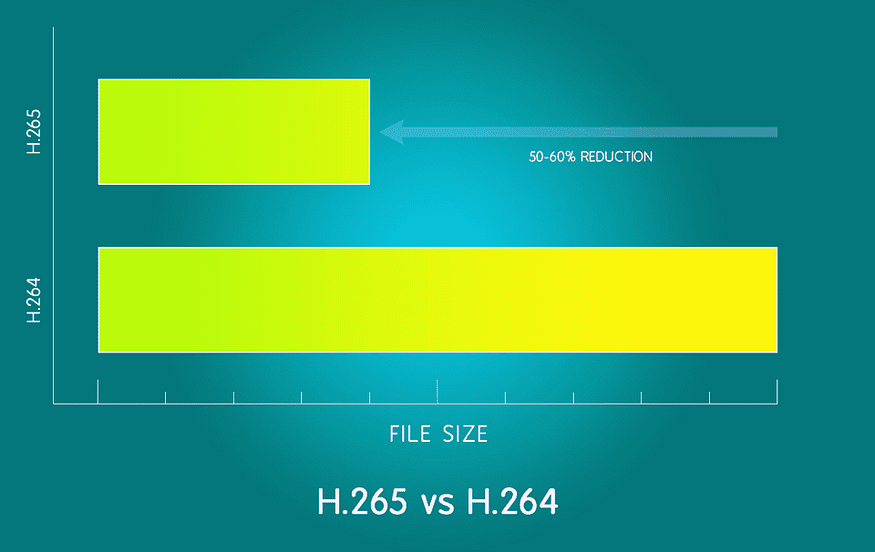
You can probably infer from the table above that H.265 is generally superior to H.264. For both encoding and transmitting, it uses half as much bandwidth as H.264 while maintaining the same level of visual quality.
Additionally, it employs more sophisticated prediction technology and contains 35 intraframe motion prediction modes, more than three times as many as AVC’s nine. All of this results in a far more effective method of video compression.
However, this does not imply that you should abandon H.264 and never look back. Despite how sophisticated H.265 codec is, it still has a number of problems.
First of all, the required gear is relatively expensive due to the computing power needed for HEVC to function. Because of this, H.265 codec is still not very common. This gap is made even wider by H.265’s rather poor device and browser compatibility. According to estimates, H.265 is supported by only 30% as many devices as H.264 and by fewer video file types.
Last but not least, you should be aware that the majority of online video platforms only accept H.264 if you intend to use an online video CMS to host, manage, and distribute your material.
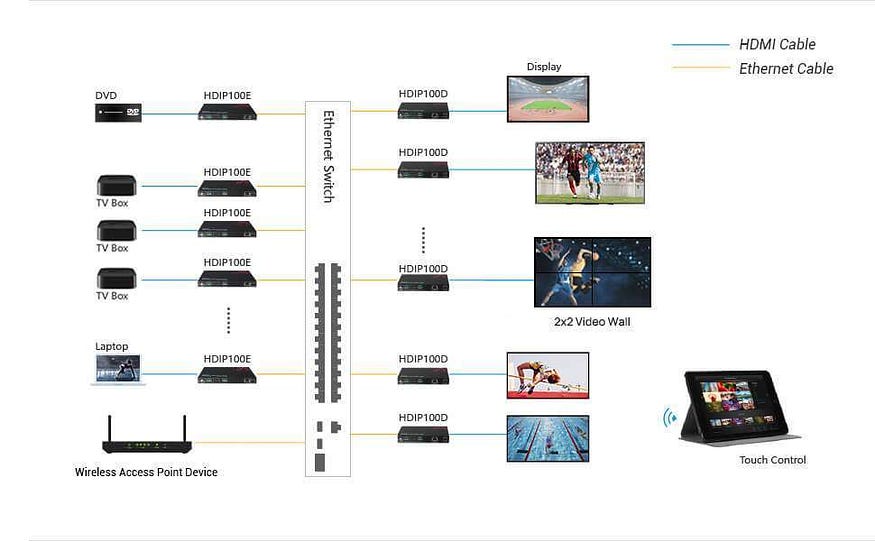
H.264/H.265 AV over IP Solution
AV over IP solutions have been widely used in various scenarios, like sports bars and universities, for digital signage, video matrix switching and video wall processing. If you are searching for a high-quality and plug-n-play H.265 AV over IP solution, AV Access HDIP100 is the one that you can’t miss.
The advanced H.265 video codec is adopted by the HDIP100 AV over IP encoder/decoder. It can work flawlessly with any universal managed or unmanaged Ethernet switch on the market. It boasts matrix switching, video wall support, easy visual control, fast seamless switching, etc. It is perfect for wide applications like sports bar, restaurant, shopping mall, retail store, house of worship, etc.
Conclusion
So H.264 vs H.265, which one should you pick? Do you want to start live streaming from the comfort of your bedroom for content creation? Then H.264 ought to be sufficient for your needs. Do you work for a major broadcaster trying to streamline the streaming procedure? Then H.265 might offer you a better value for your money.
From my perspective, H.264 codec still rules as the industry standard and isn’t going anywhere, despite its slightly inferior performance. That’s all for the blog. If you have any questions or suggestions, please feel free to leave a comment below.
12 FAQs You May Be Also Interested In
If you need more information about H.264 and H.265, please refer to the QAs below.
Is H.264 the same as MP4?
No, H.264 is a video codec, while MP4 is a container format that can hold videos encoded with various codecs, including H.264.
Is H.264 high quality?
Yes, H.264 is a high-quality video codec commonly used in various applications, including video streaming, video conferencing, and Blu-ray discs.
Does H.264 support 4K?
Yes, H.264 can support 4K video, but it may require a high bit rate to maintain quality.
Does Youtube support H.264?
Yes, Youtube supports H.264 video codec for playback.
How to change H.265 to H.264?
You can use video converter software to change H.265 to H.264 format.
How to check if my video is H.264?
You can check the file properties of your video or use a media player that displays the codec information to determine if your video is H.264.
Can I upload H.265 to Youtube?
Yes, you can upload H.265 to Youtube, but it may take longer to process and may not be playable on all devices.
Does H.265 reduce quality?
No, H.265 is designed to maintain or improve video quality while reducing file size compared to H.264.
Why Is H.265 not popular?
H.265 is not popular because it requires more processing power to decode compared to H.264, and not all devices support it.
Does H.265 use more CPU?
Yes, H.265 typically requires more CPU power to decode compared to H.264, which can affect battery life on mobile devices.
Is H.264 or H.265 better for video streaming?
H.265 is better for video streaming because it can deliver the same video quality at a lower bit rate, reducing bandwidth usage. However, it requires more processing power to decode.
Is H.264 or H.265 better for video editing?
H.264 is better for video editing because it is widely supported and can be edited faster than H.265 due to its lower decoding complexity.
More Resources
- Collection of AV Access AV over IP Solutions
- Pros and Cons of the H.265 Codec (HEVC)
- Plug-n-Play AV over IP Solution in Sports Bar and Shopping Mall
- Controlling Remote Computers with Better Scalability: KVM over IP Solutions
- Build Video Wall Within Minutes with HDIP100 Plug-n-Play AV over IP Solution
- Which is Better, AV over IP or Traditional AV?
- Video Walls: Everything You Need to Know
Original copy: https://www.avaccess.com/blogs/guides/h264-vs-h265-difference/

